Macronutrients which are Protein, carbohydrates, and fats that provide energy and nutrients for the body. (nutrients that are required daily in large quantities).They’re considered essential nutrients, meaning your body either cannot make them or cannot make enough of them. For example, proteins provide essential amino acids, while fats contain essential fatty acids. Your body utilizes these components for specific functions.

The calorie content of each macronutrient is (4):
- Carbs: 4 calories per gram
- Protein: 4 calories per gram
- Fat: 9 calories per gram
Protein
Protein is essential for building and repairing body tissues, including muscles, skin, and organs. It is made up of amino acids and also plays a role in enzymes and hormones.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the body’s main source of energy. They are broken down into glucose (sugar), which fuels physical activity and brain function. They come in forms like sugars, starches, and fiber.
Fat
Fats provide long-term energy, support cell growth, and help absorb certain vitamins (like A, D, E, and K). Healthy fats include unsaturated fats from sources like nuts, seeds, and fish.
Protein
Function:
- Builds and repairs tissues (muscles, skin, organs).
- Produces enzymes, hormones, and other body chemicals.
- Supports immune function.
Building Blocks:
- Made of amino acids (20 types; 9 are essential and must be obtained through diet).
Types:
- Complete proteins (contain all essential amino acids): found in animal products like meat, fish, dairy, and eggs.
- Incomplete proteins: found in plant-based sources like legumes, nuts, and grains (can be combined to form complete proteins).
Sources:
- Animal: chicken, fish, eggs, milk, cheese.
- Plant: lentils, beans, soy, quinoa, nuts.
Daily Need:
- Varies by age, activity level, and health status; generally around 0.8 grams per kg of body weight for adults.
Carbohydrates
Function:
- Main source of energy.
- Fuels brain, muscles, and other body functions.
- Provides dietary fiber for digestive health.
Types:
- Simple Carbohydrates – quick energy (sugar, glucose, fructose).
- Found in: sweets, soda, fruits, honey.
- Complex Carbohydrates – slow-digesting, longer-lasting energy.
- Found in: whole grains, vegetables, legumes.
- Fiber – indigestible part of plant foods that aids digestion.
- Soluble fiber: lowers cholesterol (oats, beans).
- Insoluble fiber: adds bulk to stool (whole wheat, vegetables).
Sources:
- Whole grains (brown rice, oats)
- Vegetables
- Fruits
- Legumes
- Dairy (contains lactose, a natural sugar)
Daily Need:
- 45–65% of total daily calories (based on individual energy needs).
Fats
Function:
- Long-term energy storage.
- Protects organs and insulates the body.
- Helps absorb fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K).
- Essential for hormone production and brain health.
Types:
- Unsaturated Fats – Healthy fats.
- Monounsaturated fats: olive oil, nuts, avocados.
- Polyunsaturated fats (including Omega-3 & 6): fish, flaxseeds, walnuts.
- Saturated Fats – Limit intake.
- Found in: red meat, butter, cheese.
- Trans Fats – Harmful, avoid.
- Found in: some processed and fried foods.
Sources:
- Healthy: nuts, seeds, olive oil, fatty fish.
- Less healthy: butter, ghee, high-fat meats, processed snacks.
Daily Need:
- 20–35% of total daily calories.
- Limit saturated fats to less than 10% of daily intake; trans fats should be avoided.
The recommended daily intake of protein, carbohydrates, and fat for different age groups, based on general guidelines (from organizations like the ICMR, WHO, and USDA). The exact requirements vary by gender, physical activity, and health status, but the following provides general averages:
Children (1–8 years)
| Nutrient | Amount Needed | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Protein | 13–19 grams/day | Supports rapid growth and tissue development. |
| Carbohydrates | ~130 grams/day | Should be about 50–60% of total energy. |
| Fat | 30–40% of total calories | Includes healthy fats for brain development. |
Adolescents (9–18 years)
| Nutrient | Amount Needed | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Protein | 34–52 grams/day | Boys may need more during growth spurts. |
| Carbohydrates | 130–300 grams/day | Increased due to high energy needs. |
| Fat | 25–35% of total calories | Emphasis on healthy unsaturated fats. |
Adults (19–50 years)
| Nutrient | Amount Needed | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Protein | 46g (women) – 56g (men) / day | More if physically active or training. |
| Carbohydrates | 225–325 grams/day | Should make up ~45–65% of total calories. |
| Fat | 20–35% of total calories | Saturated fats <10%, avoid trans fats. |
Older Adults (51+ years)
| Nutrient | Amount Needed | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Protein | 46–60 grams/day | May need more to maintain muscle mass and strength. |
| Carbohydrates | 180–300 grams/day | Focus on fiber-rich and low-GI carbs. |
| Fat | 20–30% of total calories | Healthy fats help manage cholesterol and brain health. |
Physically Active or Athletes (All Ages)
| Nutrient | Amount Needed | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Protein | 1.2–2.0 grams per kg body weight/day | Higher for strength or endurance training. |
| Carbohydrates | 5–7 g/kg/day (moderate activity) 7–10 g/kg/day (intense training) | Essential for energy and recovery. |
| Fat | 20–35% of total calories | Don’t drop below 15%, even during weight loss. |
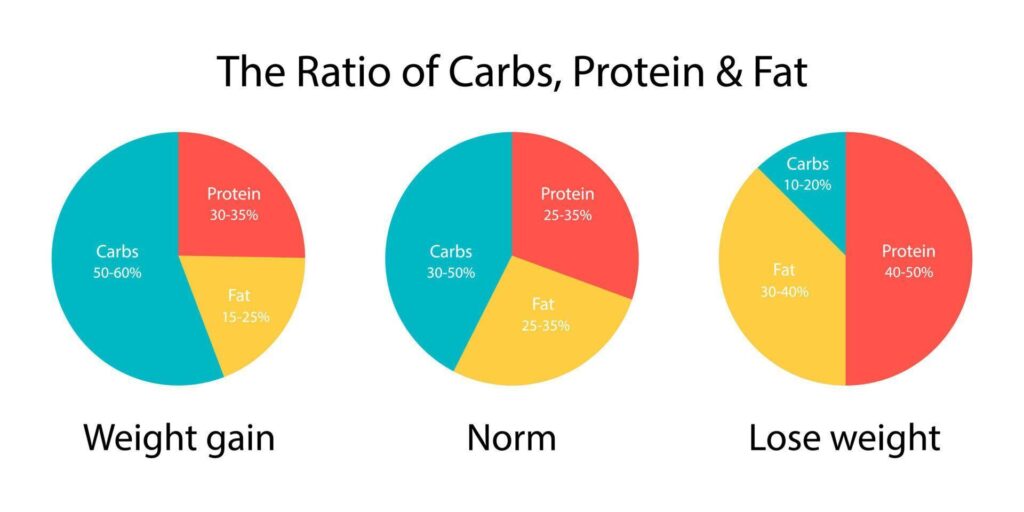
Balanced Plate: A good meal ideally includes all three – protein for repair, carbs for energy, and fat for support functions.
Macronutrient Timing: Consuming carbs and protein post-exercise aids recovery; fats before a workout may slow digestion.

This is a great explanation of the importance of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats in our diet. I appreciate how it highlights the specific roles each nutrient plays in maintaining our body’s functions. It’s useful to know that proteins are vital for tissue repair, carbs fuel energy, and fats support long-term health. The focus on healthy sources of these nutrients is also very informative. How can we effectively balance these nutrients in our daily meals to ensure optimal health? German news in Russian (новости Германии)— quirky, bold, and hypnotically captivating. Like a telegram from a parallel Europe. Care to take a peek?